Lower Back Pain in Females: Causes, Diagnosis, & Treatments
- Dr. P T Ponmani
- October 21, 2022
- No Comments
How common is lower back pain?
Lower back pain is a condition that affects many women of various age groups. However, not all women suffer due to a single exact cause or reason. Instead, there are multiple causes and conditions behind their pain.
A community-based study regarding the assessment of the prevalence of low back pain among women in India showed that the prevalence of low back pain among women in one month was 42%, which is much higher when compared to study findings of Badley et al. Another study which was conducted to estimate the prevalence and correlates of low back pain among adults aged 20 years and above in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu revealed that 1-year prevalence of low back pain among women was 52.9% commonly occurring (50%) among the age group of 41-50 years.
In general, most people experience back pain in their day-to-day life due to unhealthy lifestyles and choices. However, back pain can affect any age group or sex for various reasons and causes. As people age, the chances of getting back pain keep increasing. But lower back pain is more common and specific in women than men, and it may range from mild, intermittent pain to persistent, severe, disabling pain.
What causes back pain in women?
There are various factors and conditions which cause back pain in women. The upper and middle back pain is usually due to muscle strain, sprain, arthritis, spondylitis, poor posture, misalignment of the spine, overuse of muscle, or any injury to discs, muscles, or ligaments.
Mostly the symptoms of lower back pain in women are related to the disorders or dysfunction of their reproductive organs. Such conditions include PMS, dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, pregnancy, piriformis syndrome, sacroiliac joint dysfunction, muscle strain, sciatica, herniated disc, disc degeneration, etc.
Below we list out the causes under two broad categories
- Women-specific conditions that cause low back pain and
- Other causes
Conditions specific to women causing lower back pain
1. Dysmenorrhea

A condition where a woman experiences painful menstruation is known as dysmenorrhea. The pain is usually manageable but can be very severe in some women. The risk for dysmenorrhea increases if a woman:
- is under the age of 20
- bleeding heavily during the periods
- have a family history of dysmenorrhea
- have an underlying medical condition such asendometriosis, uterine fibroid, pelvic inflammatory disease, etc.
The pains are usually experienced in the lower abdomen, lower back, hips, and legs. The severe pain may last for a few days, and then the pain can either become dull, intense, or sharp shooting in nature.
PMS or, premenstrual syndrome, is a condition experienced by most women before their periods. However, every woman has symptoms, and they all do not suffer similarly. The premenstrual syndrome usually starts a few days before your period and ends within a day or two after the period begins.
Some of the common symptoms are:
- lower back pain
- headache
- fatigue
- bloating
- emotional imbalance
- mood swings
- food cravings
- anxiety
- trouble concentrating
2. Premenstrual dysmorphic disorder (PMDD)
PMDD, or premenstrual dysmorphic disorder, is a more severe form of PMS, where symptoms are much worse and may interrupt the daily routine. Some people with PMDD may have trouble functioning efficiently during this period because of the severity of the symptoms. However, very few women suffer from PMDD more than PMS.
Otherwise, the manifestations, like emotional, behavioural, and physical symptoms of PMDD, are very similar to PMS except for the intensity. The symptoms typically start a few days before the periods and end a few days once the periods appear.
Women with a family history of depression and other mood disorders or a family history of PMDD are at a high risk of getting premenstrual dysmorphic disorder.
3. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a severe uterine condition where the lining tissue of the uterus, known as the endometrium, spills out, spreads, or grows outside the uterus within the pelvic cavity. These tissues attach themselves to other nearby pelvic organs and undergo the same changes as it does inside the uterus.
The symptoms are:
- Excruciating menstrual cramps
- Pain during or after sex
- Lower back ache and pelvic pain
- Pain with bowel movements or urination during the period
- Bleeding or spotting between two periods.
- Women with endometriosis also suffer from digestive problems like bloating and diarrhoea during the period. In addition, endometriosis may make getting pregnant harder for a woman.
4. Pregnancy

Back pain is usually a common problem during pregnancy. It happens due to the shift in the centre of gravity as more weight gain occurs.
Most women experience back pain around the fifth and seventh months of pregnancy, but it can start much earlier. In addition, women are more likely prone to back pain during pregnancy if they already have some other lower back problems. This pain may radiate into the thighs and legs.
Also Read The Complete Guide to Medicine During Pregnancy and The Expectant Mother’s Health
5. Pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID)

Many women experience chronic back pain and discomfort persistently. It may be due to any pelvic inflammatory condition. The most common complaints are lower back aches, abdominal cramps and pain, low-grade fever, and vaginal discharge. Pelvic inflammatory diseases are usually caused by a particular bacterial infection which could become severe if left untreated.
6. Piriformis syndrome

The piriformis is a thick muscle located deep within the other muscles of the buttock region. It is known as piriformis syndrome when a woman suffers pain from sudden or intermittent spasms of the piriformis muscle. This syndrome may be due to hormonal and pregnancy-related changes in the woman.
The symptoms of piriformis syndrome are- difficulty sitting for an extended period, radiating pain from the back of the thigh to the legs, and chronic pain in the back, bottom, and hips area, which worsens during any movement of the hip joint.
7. SI joint dysfunction
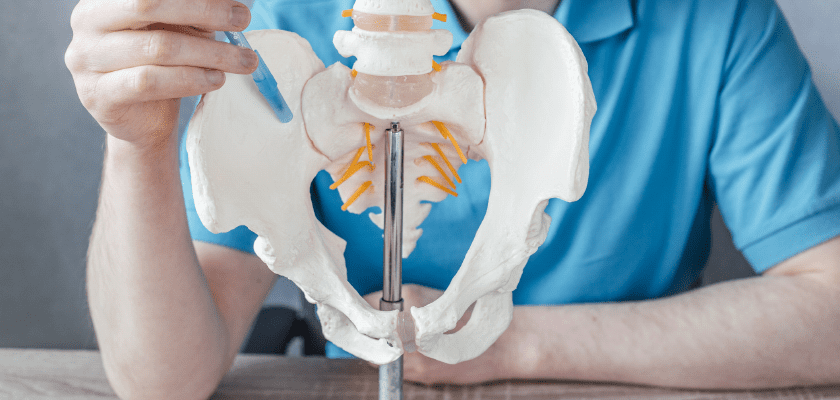
The sacroiliac joint connects the lower part of the vertebra, the sacrum, to the pelvis. Pain radiating from this area is called sacroiliac joint dysfunction or sacroiliitis. It is one of the major causes of lower back pain.
Since women have a smaller sacroiliac joint than men, there is a higher level of stress that has to be borne by the joint. Due to this, women suffer severe lower back pain that radiates down the thigh towards the knee joint and dull, constant pain in the buttocks.
8. Coccydynia
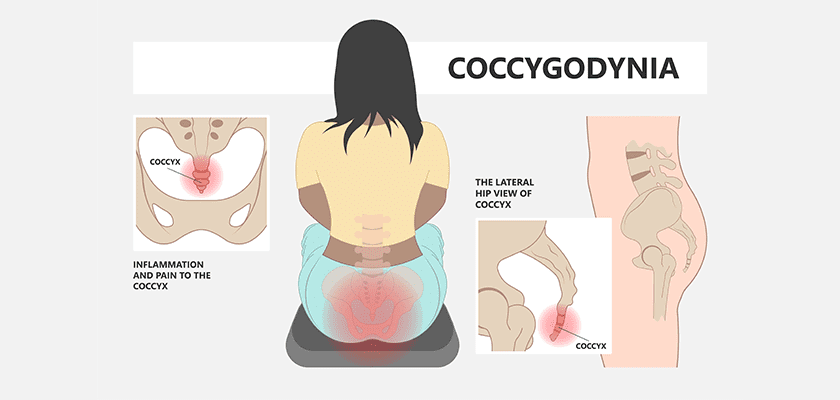
Pain in the coccyx is called coccydynia. It is primarily due to any injury or trauma to the coccyx. It is much more common in women due to smaller pelvis and childbirth-related damages. The symptoms include pain while sitting down, sitting on hard surfaces, standing up from a seated posture, and leaning backwards while sitting.
9. Back injuries
Injuries and trauma like strain and sprain are the most common cause of back pain in many women due to the overuse of muscles, such as heavy lifting or sudden movement, causing middle or lower back pain. In addition, these muscle overuse injuries are also common during pregnancy.
10. Cancers
Certain spinal and uterine cancers (like cancer of the cervix and endometriosis) can cause severe and long-standing back pain. They can be a form of referred pain from metastatic breast or lung cancer.
Also Read Homeopathic Medicine for Back Pain
Other causes of lower back pain
There are lower back pains that can affect anyone despite the sexes. A few of the most common causes and conditions are:
1. Kidney infection
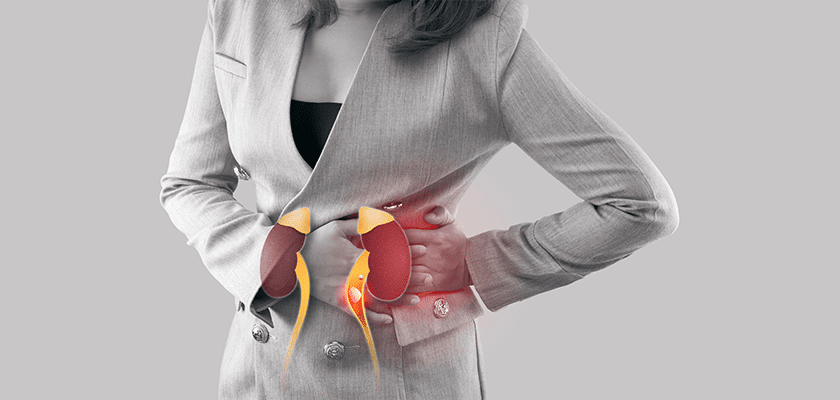
Also called pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys and urinary tract. The symptoms are lower abdominal pain and backache, especially in the flanks and groin. Sometimes it is also associated with fever and chills, and frequent urination.
2. Sciatica
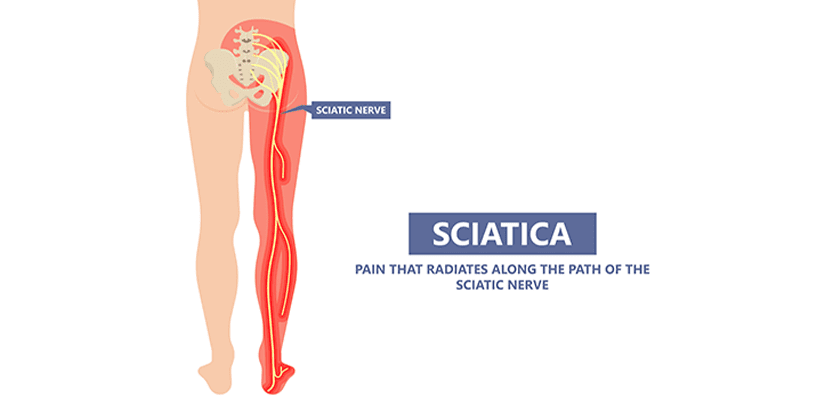
Sciatica is a condition caused due to compression or injury to the sciatic nerve. This nerve travels from the lumbar plexus through the buttocks and down the back of the legs.
Sciatica has become one of the ordinary conditions due to a sedentary lifestyle. It causes sharp, electric shock-like pains in the lower back shooting down to the leg. Usually, it is associated with numbness and weakness.
3. Herniated disc
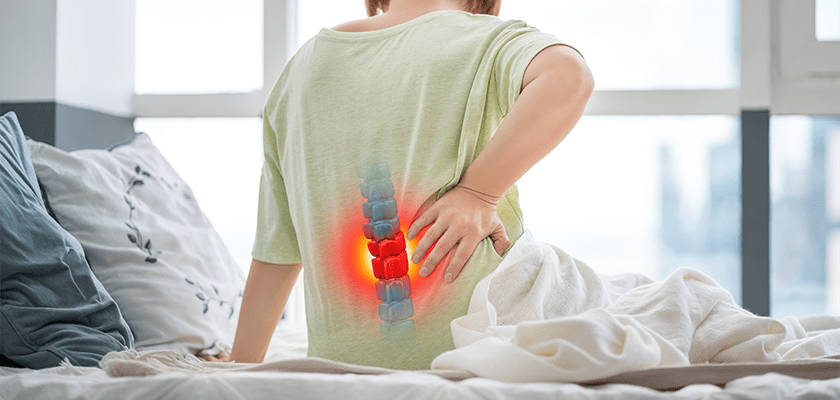
A herniated vertebral disc is a condition where any disc that cushions the vertebrae gets compressed and bulges outward. It eventually causes the disc to rupture. Pain arises due to the bulging disc pressing on a nerve.
An injury can also cause a herniated disc. But, again, the occurrences and chances increase as a person ages.
The bulging disc or disc slip occurs when the cushion-like cartilage bulges out and compresses the neighbouring nerves. The risk increases as a person ages as these cushion-like discs become dehydrated and stiff. The compression from the bulging disc causes shooting pains in the back which radiates to the legs. In addition, traumatic accidents or sudden movements can also cause this problem.
4. Sedentary lifestyle

Lifestyle, job, and habits are common causes of back pain. For example, when a person sits for a long time for work or is too lazy to move, they may suffer from back pain, stiffness, or uneasiness. Likewise, when a person sits for a long time, the back muscles may get locked due to inactivity, and cause pain. So, one must stretch their muscles whenever there is time for relaxation.
5. Incorrect posture

Prolonged screen time can affect posture, and poor posture can cause back pain or increase the existing pain. Screen time and standing or walking style can also affect a person’s posture. A wrong posture increases the strain on the muscles and ligaments, resulting in back pain.
6. Muscle sprain
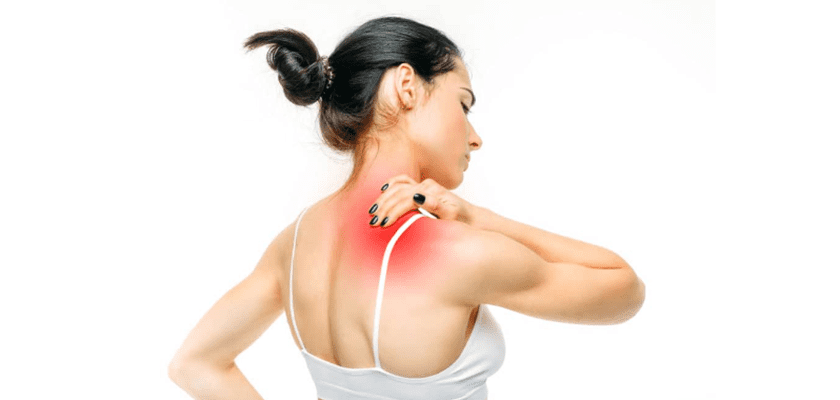
It is common for people when they lift overweight in improper form or sudden moves. Symptoms include pain and stiffness of muscles. Rest, and if needed, painkillers can ease the complaints.
7. Muscle strain

- A muscle strain or ligament tear can be caused by
- Actions such as heavy weight-lifting
- Bending or twisting the body awkwardly
- A sudden movement
- Overstretching of the muscle or ligament, etc., sometimes causes back spasms.
8. Spinal osteoarthritis

The fibrous cartilage between the joints is thinned and worn out in this condition. Due to the loss of this cushioning effect provided by the cartilage, the bones may rub together, causing friction and severe pain.
Common symptoms of spinal osteoarthritis include back stiffness and pain in the morning and pain in your lower back area, upper back, thighs, groin, and buttocks.
The disc can degenerate or wear out due to old age, injuries, or repetitive motions. The pain may extend from the buttocks to the legs from the back. The pain is usually constant and dull and may be relieved by rest.
The condition usually does not cause many symptoms, but some people might experience severe pain.
What causes pain in the lower left back?
Some medical conditions that cause pain in the lower left back are renal calculi, kidney diseases, pancreatitis, ulcerative colitis, spinal injuries, muscle or ligament sprains, etc. In addition, females may experience severe left lower backache due to conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, any tissue masses in the uterus or ovary, and during pregnancy.
What causes back pain on the lower right side?
Pain on the lower right side is a common symptom in conditions such as kidney stones, appendicitis, any disorders or large intestines, gallstones, liver problems, mechanical causes, etc. The situation specific to women is pregnancy, endometriosis, any tumours of the uterus or ovaries, etc.
Risk factors for lower back pain
Some people are more prone to develop lower back pain than others. A few of the risk factors are:
- Age: Older people are more prone to back pain as the disks weaken and cartilage and bones degenerate.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on joints and discs, leading to pain.
- Weak abdominal muscles that cannot support the spine can lead to back strains and sprains.
- A sedentary lifestyle, occupation, and lack of physical activities can increase the risk of back pain.
- Due to spinal misalignment, severe back pain may result from structural conditions, such as scoliosis.
- Hereditary and genetics also play a vital role in people with a family history of osteoarthritis, cancer, and other degenerative disorders.
- Depression can also cause back pain.
How is lower back pain diagnosed?
Before reaching a diagnosis, a proper physical exam, medical history, and the person’s current symptoms should be considered. Additionally, imaging tests, including CT scans, X-rays, MRIs, and ultrasounds, should be recommended to determine the cause of lower back pain.
When to see a doctor
In some cases, it is essential to visit a doctor and undergo some tests and investigative procedures to determine the cause of the back pain. It is advisable to seek immediate medical attention as soon as possible if you experience the following symptoms:
- You’re unable to stand or walk
- A fever accompanies your back pain,
- Unable to control your bowel or bladder
- Have pain, numbness, or tingling in your legs
- The pain extends down your legs
- Have severe abdominal pain
- Back pain is severe and interferes with your daily life
- Have symptoms of endometriosis
- Have pain during pregnancy with vaginal bleeding
- You have back pain after a fall or accident
What is the fastest way to cure lower back pain?
Treatment for lower back pain varies from person to person, depending on the cause, which is why an accurate diagnosis is vital for providing faster relief to the person.
The conventional modes of treatment for most menstrual-related problems are:
- Surgery for severe endometriosis involves the removal of the endometrial tissue from areas where it has grown outside the uterus.
- TENS stands for transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation. This procedure delivers electric shocks to the skin, which in turn helps release natural endorphins from the body to reduce pain.
- Acupuncture and acupressure are complementary therapies that focus on applying pressure to various body areas to reduce pain and promote healing.
- If the scarring and damage are extensive enough, it could require a complete hysterectomy.
The treatments for other lower back pain are:
- Medications: prescription drugs to relieve pain, relax muscles, and prevent back spasms.
- Physiotherapy: it helps to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Hands-on manipulation: can relax tight muscles, reduce pain and improve posture and alignment. Massage therapy can also help to relieve back pain and movement.
- Injections: Steroid injections relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: some injuries and conditions may need surgical repair.
-
 B&T OLMUVSale Product on sale
B&T OLMUVSale Product on sale₹130.00₹106.60Rated 4.20 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings -
 Dr Willmar Schwabe India Rück-PainSale Product on sale
Dr Willmar Schwabe India Rück-PainSale Product on sale₹205.00₹168.10Rated 4.85 out of 5 based on 13 customer ratings -
 Freedom from Joint PainSale Product on sale
Freedom from Joint PainSale Product on sale₹620.00₹508.40 -
 Dr Willmar Schwabe India Alpha-MPSale Product on sale
Dr Willmar Schwabe India Alpha-MPSale Product on sale₹135.00₹110.70Rated 4.83 out of 5 based on 6 customer ratings
7 Home remedies for general lower back pain in Women
The following simple steps may help to ease the pain:
1. Heating Pad

A heating pad applied to the back can boost blood circulation, providing oxygen to the muscles in your back.
2. Warm Bath/Massage

A warm bath or a warm massage can improve circulation and reduce muscle pain and stiffness.
3. Staying Active

Staying active can improve blood circulation and reduce the tension in the muscles.
4. Exercises

Regular stretching exercises can help reduce lower back pain.
5. Use Ice Packs

Ice packs can also reduce inflammation, muscle strain, or injury.
6. Cushion

Placing a cushion between the knees while sleeping can help reduce back pain and abdominal discomfort.
7. Back Supports

Using a chair with proper back support may help ease back pain when sitting.
Also Read Homeopathic Pain Relief Spray: How Does Pain Relief Spray Work?
Conclusion
In females, lower back pain during menstrual periods is a common symptom of period-related conditions, such as PMS. The pain may be more severe with conditions like PMDD, dysmenorrhea, or endometriosis. Treatments for such severe lower back pain may include painkillers, NSAIDs, alternative therapies, and surgery.
Many home remedies can help ease lower back pain, including heat, rest, and gentle exercise. However, immediate medical attention should be given when the pain does not subside for a long time.
Other conditions and certain underlying factors can also cause lower back pain in women, such as muscle sprain and strains, sciatica, or a herniated disc that affects anyone regardless of age or sex.
The treatment usually depends on the pain’s intensity, cause, and nature. In many cases, the pain improves with home care. But, if the back pain persists or gets severe, it is good to seek medical attention for possible diagnosis and immediate treatment.
Usually, people with simple back strains and sprains recover in a few days and do not have long-term complications. However, some people have chronic back pain that doesn’t get better even after several weeks or months.
On the other hand, in older people with certain degenerative conditions, such as arthritis and osteoporosis, the pain and other symptoms get worse over time. However, proper timely management of the symptoms can prevent serious troubles.
FAQs: Back Pain Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ 1. What are the three categories of back pain?
Back pain is most commonly categorized into three types: axial pain, referred pain, and radical pain.
FAQ 2. Can back pain affect your whole body?
Yes. The back pain can radiate upwards and downwards, affecting the whole body.
FAQ 3. How do I know if my lower back pain is serious?
It can be identified by a thorough check-up and examination followed by various tests recommended by your physician.
FAQ 4. How should I sleep with lower back pain?
You can sleep on the side with a cushion stuffed between the knees or follow the physician’s advice.
FAQ 5. How long does back pain last?
The lower back pain can last a few days to a few weeks. The intensity and duration of pain also depend on the diagnosis.
FAQ 6. What organ is located in the lower back area?
The kidneys are located on the lower back, on either side of the spine.